
APEC VIRTUAL SUMMIT 2020
APEC VIRTUAL SUMMIT: REGIONAL ECONOMIC FORUM
Recently, a virtual meeting of the 21-member Asia-Pacific Economic Cooperation (APEC) forum was held. The meeting was hosted by Malaysia. New Zealand will also host next year's APEC meetings virtually due to the pandemic.
ASIA-PACIFIC ECONOMIC COOPERATION (APEC)
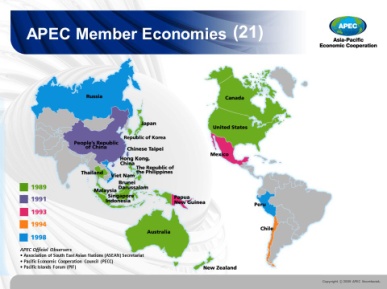
The Asia-Pacific Economic Cooperation (APEC) is a regional economic forum established in 1989 to leverage the growing interdependence of the Asia-Pacific. The basic concept behind the formation of this regional economic forum was to create greater prosperity for the people of the region by promoting balanced, inclusive, sustainable, innovative and secure growth and by accelerating regional economic integration.
FUNCTIONS OF THE APEC

Multilateral Economic Forum: It operates as a cooperative, multilateral economic and trade forum. It is the only international intergovernmental grouping in the world committed to reducing barriers to trade and investment without requiring its members to enter into legally binding obligations. APEC achieves its goals by promoting dialogue and arriving at decisions on a consensus basis, giving equal weight to the views of all members.
Host Economy: Every year one of the 21 APEC Member Economies plays host to APEC meetings and serves as the APEC Chair. The APEC host economy is responsible for chairing the annual Economic Leaders' Meeting, selected Ministerial Meetings, Senior Officials Meetings, the APEC Business Advisory Council and the APEC Study Centres Consortium. Until 2009, the host has also filled the Executive Director position at the APEC Secretariat. From 2010, the appointment will be made on a fixed-term basis (3 yrs) and will be open to candidates from all Member Economies.
Funding: It is not a donor organization but member economies provide voluntary contributions to support projects that advance APEC's trade and investment liberalisation and facilitation goals and to meet capacity-building needs, especially for APEC developing economies.
APEC & India: India had requested membership in APEC, and received initial support from the United States, Japan, Australia and Papua New Guinea. Officials have decided not to allow India to join as India does not border the Pacific Ocean, which all current members do. India was invited to be an observer for the first time in November 2011.
Reasons for India to join APEC: India will be more integrated with the global economy since APEC economies constitute an important trading bloc in the world. It will help India bargain and negotiate a better deal with the countries of the Asia-Pacific region.
AREAS OF CONCERNS IN THE SUMMIT
With growth in the Asia-Pacific region expected to decline by 2.7% this year, from a 3.6% growth in 2019, APEC's focus was on accelerating economic recovery and developing an affordable vaccine.
Focus Areas: Trade and investment, Digital Economy and Technology, Structural Reform, Economic and Technical Cooperation and Thematic and institutional matters. APEC leaders adopted the Putrajaya Vision 2040, a new 20-year growth vision to replace the Bogor Goals named after the Indonesian town where leaders agreed in 1994 to free and open trade and investment.
Recognised the importance of a free, open, fair, non-discriminatory, transparent and predictable trade and investment environment to drive economic recovery at such a challenging time (Covid-19). Discussed the Free Trade Area of the Asia-Pacific (FTAAP) agenda and the APEC Internet and Digital Economy Roadmap (AIDER). China has become the main driving force behind the grouping after the United States began withdrawing from multilateral bodies during Trump's presidency. But Trump made the surprise decision to take part in this year's event, after not participating at APEC since 2017.
CHINA'S STAND IN THE SUMMIT
It vowed to keep its “super-sized” economy open for business and warned against protectionism as the world battles the Covid-19 pandemic. It needs to be noted that Trump’s "America First" policy has alienated trading partners. After the signing of the world’s largest trade pact ‘Regional Comprehensive Economic Partnership (RCEP)’, China is trying to set the agenda for global commerce. Although China is promoting openness in trade, its own actions go against it, for example: Australian exports of beef, wine and barley to China, their biggest market, have been restricted.
CONCLUSION
APEC has been criticised for promoting free trade agreements that would impose restrictions on national and local laws, which regulate and ensure labour rights, environmental protection and safe and affordable access to medicine. According to the organisation, it is "the premier forum for facilitating economic growth, cooperation, trade and investment in the Asia-Pacific region" established to "further enhance economic growth and prosperity for the region and to strengthen the Asia-Pacific community". The effectiveness and fairness of its role has been questioned, especially from the viewpoints of European countries that cannot take part in APEC and Pacific Island nations that cannot participate but stand to be affected by its decisions.
QUESTIONS (1-5)
Q.1 Which of the following countries has hosted the virtual meeting of the 21-member Asia-Pacific Economic Cooperation (APEC) forum?
A. Malaysia: ANSWER
B. New Zealand
C. Thailand
D. Vietnam
Q.2 Which of the following statements regarding Asia-Pacific Economic Cooperation summit (APEC) is correct?
A. (APEC) is a regional economic forum established in 1989.
B. Is a Free Trade cooperation between the littoral countries of Pacific Ocean.
C. India was an observer for the first time in November 2011.
D. All of the above: ANSWER
Q.3 Which of the following is not an important pillar of Asia-Pacific Economic Cooperation?
A. Trade and Investment Liberalization
B. Economic and Technical cooperation
C. Military Assistance: ANSWER
D. Business Facilitation
Q.4 In which of the following years India was invited to be an observer for the first time in APEC Regional forum?
A. 2010
B. 2011: ANSWER
C. 2012
D. 2013
Q.5 Which of the following countries is not in the list of 21-members of Asia-Pacific Economic Cooperation (APEC)?
A. China
B. United States of America
C. Japan
D. India













0 Comment