
NATO VS CSTO
SITUATIONS IN ARMENIA AND AZERBAIJAN CONFLICT
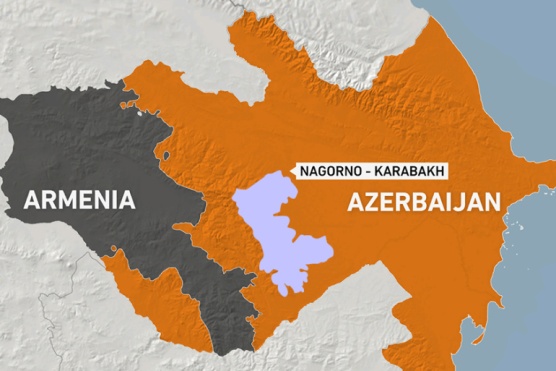
Recently, three decades-old unresolved ethno territorial conflict between Armenia and Azerbaijan over Nagorno-Karabakh flared up once again. The conflict is between two relatively small countries and is territorial in nature. However, several regional and global players particularly Russia, Europe, Turkey and Iran are also involved to secure their strategic, security and economic interests in the region. As the strategic importance of the region is derived from energy exports, the stability of the region is very important for regional growth and oil importing countries like India. Further, the conflict may cause geopolitical unrest in the region which is already suffering from the Covid-19 pandemic. Therefore, regional powers must strive to find a diplomatic solution to the problem and prevent the clash turning into a full blown regional conflict.
INTERVENTION OF REGIONAL POWERS INTO THE CONFLICT
What makes the clashes now far more dangerous is the external intervention. Turkey has called Armenia a threat to peace in the region, the Azeris and Turks share ethnic and linguistic bonds. Also, the pre-Soviet Azerbaijan was a local ally of the Ottomans when they invaded Transcaucasia in the last leg of World War I. For Turkey, which, under President Recep Tayyip Erdoğan, is trying to expand its geopolitical reach to the former Ottoman regions, the conflict over Nagorno-Karabakh is an opportunity to enter the South Caucasus. Turkey also has a particularly bad relationship with Armenia. But its problem is that Armenia is a member of the Russia-led Collective Security Treaty Organization (CSTO). Russia enjoys good economic and defence ties with both Armenia and Azerbaijan. But Armenia, as a CSTO member and host to a Russian military base, has more weight. In a wider conflict, Armenia could trigger Article 4 of the CSTO treaty and ask for Russian help. And if Moscow responds favorably, that would pit Russia against Turkey, a NATO member. Russia, already involved in military conflicts in Syria, Ukraine and Libya, may not like opening another front. That is why it has re-emphasized its neutrality and hosted talks in Moscow for a truce. But it will be forced to take sides if the conflict spills into Armenia. Both sides should understand the volatile situation and call off the hostilities. Nagorno-Karabakh has in the past witnessed large-scale ethnic violence. Instead of risking a regional war, Azerbaijan, Armenia and the Karabakh rebels should go back to the ceasefire and open up diplomatic channels.
NORTH ATLANTIC TREATY ORGANISATION (NATO)

The North Atlantic Treaty Organization (NATO) also called the North Atlantic Alliance is an intergovernmental military alliance between 30 North American and European countries. The organization implements the North Atlantic Treaty that was signed on 4 April 1949. NATO constitutes a system of collective defence whereby its independent member states agree to mutual defence in response to an attack by any external party. NATO's Headquarters are located in Evere, Brussels, Belgium, while the headquarters of Allied Command Operations is near Mons, Belgium.
The North Atlantic Treaty Organization was created in 1949 by the United States, Canada, and several Western European nations to provide collective security against the Soviet Union. NATO was the first peacetime military alliance the United States entered into outside of the Western Hemisphere. NATO's fundamental goal is to safeguard the Allies' freedom and security by political and military means. NATO remains the principal security instrument of the transatlantic community and expression of its common democratic values.
The United States and 11 other nations establish the North Atlantic Treaty Organization (NATO), a mutual defense pact aimed at containing possible Soviet aggression against Western Europe. NATO stood as the main U.S.-led military alliance against the Soviet Union throughout the duration of the Cold War. The September 11 attacks in the United States caused NATO to invoke Article 5 of the NATO Charter for the first time in the organization's history. The Article states that an attack on any member shall be considered to be an attack on all.
MEMBERSHIP OF THE ALLIANCE
At present, NATO has 30 members. In 1949, there were 12 founding members of the Alliance: Belgium, Canada, Denmark, France, Iceland, Italy, Luxembourg, the Netherlands, Norway, Portugal, the United Kingdom and the United States. Later the other member countries who also joined the alliance are Greece & Turkey (1952), Germany (1955), Spain (1982), the Czech Republic, Hungary & Poland (1999), Bulgaria, Estonia, Latvia, Lithuania, Romania, Slovakia and Slovenia (2004), Albania and Croatia (2009), Montenegro (2017) and North Macedonia (2020). So, the most recent member state to be added to NATO was North Macedonia on 27 March 2020. NATO currently recognizes Bosnia and Herzegovina, Georgia, and Ukraine as aspiring members.
COLLECTIVE SECURITY TREATY ORGANIZATION (CSTO)

The Collective Security Treaty Organization is an intergovernmental military alliance that was signed on 15 May 1992. The CSTO grew out of the framework of the Commonwealth of Independent States, and first began as the CIS Collective Security Treaty (CST) which was signed by Armenia, Kazakhstan, Kyrgyzstan, Russian Federation, Tajikistan and Uzbekistan, in the city of Tashkent. Azerbaijan signed the treaty in September 1993, Georgia in December 1993 and Belarus in December 1993. The treaty came into effect in April 1994.
The CST was set to last for a 5-year period unless extended. In April 1999, only six members of the CST signed a protocol renewing the treaty for another five-year period – Azerbaijan, Georgia and Uzbekistan refused to sign and withdrew from the treaty instead. At the same time Uzbekistan joined the GUAM group, established in 1997 by Georgia, Ukraine, Azerbaijan, and Moldova, and largely seen as intending to counter Russian influence in the region. Uzbekistan later withdrew from GUAM in 2005 and joined the CSTO in 2006 in order to seek closer ties with Russia. In June 2012, Uzbekistan suspended its membership in the CSTO. So, the Current CSTO members are Armenia, Belarus, Kazakhstan, Kyrgyzstan, the Russian Federation and Tajikistan. Afghanistan and Serbia hold observer status in the CSTO.
It was decided to transform the CST into a full international organization, the Collective Security Treaty Organization (CSTO) at the Moscow session of the Collective Security Treaty in 2002.
AIMS AND OBJECTIVES
The key objectives of the CSTO include the provision of national and collective security & Foreign policy coordination. It also has the aim of development of cooperation in the counteraction to modern challenges and security threats, such as international terrorism, drug trafficking, illegal migration etc. It was decided to transform the CST into a full international organization, the Collective Security Treaty Organization (CSTO) at the Moscow session of the Collective Security Treaty in 2002.
COMPARISON BETWEEN NATO & CSTO
The comparison between the two military alliances on the basis of membership is that NATO considers expanding its membership while CSTO doesn't.
Comparing the two on the ground of weapon sales, NATO member states do not sell arms to a country which is regarded as a potential military adversary to the member states while CSTO (Russia and Belarus) provide nearly 85% weapon to Azerbaijan. It is important to note that Azerbaijan is not a member state of CSTO and has disagreements with Armenia (one of the member states of CSTO).
If we compare the two military alliances on the basis of an armed attack, the Article 5 of the NATO requires all the member states to come to the aid of any member state subject to an armed attack. It was invoked for the first time after the 9/11 attacks on the United States. On the other hand, CSTO in its Article 3 states the protection on a collective basis of independence, territorial integrity and sovereignty of the member states. Also, the member states are not legally bounded but can voluntarily participate in case of an armed attack over its Member State.
QUESTIONS (1-5)
Q.1 Azerbaijan, a muslim majority country is supported by Turkey in Armenia & Azerbaijan Conflict. So, Turkey is member of which of following alliances?
A. Islamic Military Alliance
B. North Atlantic Treaty Organization: ANSWER
C. South Atlantic Peace and Cooperation Zone
D. Collective Security Treaty Organization
Q.2 North Atlantic Treaty Organization which is an intergovernmental military alliance between the nations is headquartered at which place?
A. Geneva, Switzerland
B. New York, USA
C. Washington DC, USA
D. Brussels, Belgium: ANSWER
Q.3 Collective Security Treaty Organization a Military Alliance which was signed in May 1992 and aims at collective and national security is headquartered in ___________?
A. Minsk, Belarus
B. Nur Sultan, Kazakhstan
C. Moscow, Russia: ANSWER
D. Vladivostok, Russia
Q.4 How many countries are the members of the military alliances of North Atlantic Treaty Organization & Collective Security Treaty Organization respectively?
A. 25 & 5 members respectively
B. 28 & 6 members respectively
C. 30 & 6 members respectively: ANSWER
D. 32 & 8 members respectively
Q.5 From the followings pairs of the countries, which two countries are not the part of CSTO?
A. Uzbekistan, Azerbaijan: ANSWER
B. Armenia, Kazakhstan
C. Belarus, Kyrgyzstan
D. Russia, Tajikistan
Q.6 Which article of the NATO charter states that an attack on any member shall be considered to be an attack on all?
A. Article 3
B. Article 4
C. Article 5: ANSWER
D. Article 6












0 Comment